SOLAR Energy

➡️ Solar Energy – Harnessing the Power of the Sun
Solar power is now the cheapest source of renewable energy, with prices dropping 90% since 2010. It is now cheaper to produce than gas! This clean, sustainable energy harnesses the sun's rays, enables the green energy transition, and allows us to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.
Find essential information on:
- Solar power news and key platforms
- Solar farms and huge solar projects
- Large solar companies
- Feed-in Tariffs and Smart Export Guarantee
- Guide to photovoltaics
- Solar energy storage
- Solar cookers
- Solar energy costs
- Important articles
A common misconception of solar power is that panels need sunlight to operate. In truth, they only need daylight, making them versatile and practical in most places on the planet.
The technology primarily used to capture and convert solar energy includes photovoltaic (PV) panels and solar thermal systems. PV panels convert sunlight directly into electricity, while solar thermal systems use the sun's heat to produce thermal energy, which can then be used for heating or converted into electrical power.
After the initial startup costs, energy produced through solar is not only free, but excess energy can be sold back to the grid using schemes such as the Smart Export Guarantee in the UK. Solar panels require little maintenance and can last up to 25 years.

Advantages of Solar Energy
- Renewable and infinite: The sun is the most abundant energy source on the planet, unlike fossil fuels, the power generated by the sun will never run out.
- Environmentally friendly: Solar power does not produce greenhouse gases nor contribute to air pollution, helping us to reduce climate change.
- Reduction in electricity costs: Once installed, solar panel systems can reduce energy bills by 50–70%.
- Low maintenance: Solar panels require minimal maintenance and have a long lifespan.
- Decentralised energy generation: Solar energy enables independence from the power grid which increases energy efficiency and provides greater control at a local level.
- Job creation: The solar industry accounts for more than a third of the total work force in the renewable sector equating to 4.9 million jobs in research, development, production, installation, and maintenance.
- Solar power in international development: Solar power contributes towards the Sustainable Development Goals by bringing clean energy to communities, creating jobs, and helping to protect the environment.
Disadvantages of Solar Energy
- High initial investment cost: The installation of solar panels, inverters, batteries, and wiring adds up. The average cost to build a solar farm in the UK is £375,000 per megawatt-hour (MWh) of electricity produced. in 2024, the average cost for a homeowner to purchase and install solar panels in the UK was between £2,500 - £10,500 depending on the size of the system.
- Weather dependent: Cloudy and rainy days will affect the efficiency of solar energy production. For this reason, solar energy can only reach maximum efficiency in specific geographical regions with long hours of sunlight.
- Environmental impact of manufacturing: The mining of minerals required to build solar panels, although less damaging than fossil fuels, is still highly damaging to local areas, creates pollution, and greenhouses gases. These mines are often in developing countries and create a myriad of problems for communities including large-scale displacement and heavy metal contamination of water supplies.
- Resource requirements: The huge increase in solar panel production has created a large demand for rare earth minerals resulting in an increase in the mining of silicon, silver, aluminium, and copper – all finite sources. The availability of these raw materials may not be sufficient to meet future demand.
- Storage and grid integration: A lack of standardisation complicates integrating new solar developments to the grid, efforts to improve connection are being outpaced by renewable energy development. Without careful management, fluctuations in energy supply can create grid instability.

Leading Solar Power Countries
As the clear frontrunner in the energy transition, solar energy is being embraced all over the world as nations attempt to hit their clean energy targets, reduce their carbon emissions, and minimise dangerous levels of air pollution.
Currently valued at $250 billion, the solar power market is estimated to be worth $400 billion by 2032. Below we highlight the top 5 solar energy producing countries:
CHINA
Leading the solar revolution, China has a whopping solar capacity of 392 GW dominating 37% of the global market. They also dominate the list for solar panel manufacturers producing 77% of the world's solar panels.
China also takes the top spot as the largest single country contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions. China’s solar energy boom is driven by the necessity to meet its climate targets, huge investment, technological advancements, and supportive governmental subsidies.
It is estimated that by 2028, 60% of the worlds renewable energy will be produced in China.
U.S.A.
Taking second place, the U.S. has a solar capacity of 110 GW and is expected to increase to 378 GW by 2028. The country boasts vast areas of land abundant in sunlight especially in California, Arizona, and Texas where the majority of solar energy production takes place. Interestingly, the U.S. is also the second largest producer of greenhouse gases and is aiming for a 100% clean energy grid by 2035.
JAPAN
With a total installed capacity of 79 GW Japan takes third place. By 2025 the Japanese government will require all new homes to be installed with solar panels. They have invested huge amounts into the development of space-based solar power and flexible solar cells.
GERMANY
As the largest solar energy producer in Europe, Germany takes fourth place globally with a solar capacity of 66 GW. Germany has long been a pioneer in the renewable energy sector and the Russian war in Ukraine has prompted a further switch away from reliance on oil and gas.
Germanys performance in the solar power sector is even more impressive given their limited availability to all year-round sunlight. In the past, the government supported the sector through a series of subsidies, tax exemptions, favourable feed-in tariffs, and attractive funding opportunities for investors.
INDIA
India’s potential for solar energy production is vast. This huge country has an abundance of suitable land and enjoys long hours of sunlight all year round. Their current solar capacity is 62 GW. They have also emerged as a pioneer in off-grid systems to bring energy to many rural communities aiding their socio-economic development and helping to reduce inequalities in remote areas.
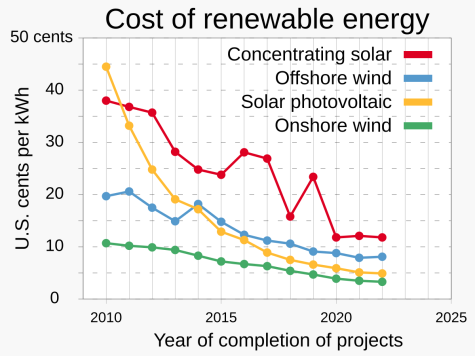
Solar Energy - The Cheapest Energy Source in the World
As the demand for solar energy systems has grown, so has the scale of production. Large scale manufacturing has allowed for more efficient production reducing material and labour costs, and the cost of is expected to keep falling. Renewable energy and climate experts are hailing this as a huge win against the fossil fuel industry which is becoming economically unviable.
The rapid growth of the solar power sector has resulted in manufacturers creating stockpiles with capacity at nearly twice that of demand. This oversupply, especially in China who are the world's largest producers of solar cells, has caused prices to crash. Bad news for manufacturers, but great news for facilitating the global energy transition.
A stumbling block for the solar sector was always the price of solar energy storage. Due to commercialisation and wider deployment of such systems, the cost of lithium-ion batteries has also seen reductions.

Solar Power for a Better World
The immense power of the sun exceeds humanities energy needs several times over. Governments are waking up to the vast potential of the solar sector. At current growth rates, solar power will make up more than half of all global electricity generation by 2050.
We must ensure that the extraction of raw materials needed to produce solar technology is done sustainably and with minimum impact. With increased efficiency and strong environmental regulations, the solar sector could be one of the best tools we have in achieving goal 7 of the SDGs by 2030 -
“Ensuring access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all.”
Solar power plays an important role in the development of emerging countries. 675 million people still do not have access to electricity - Four out of five of them are in Sub-Saharan Africa. One in four people still use unsafe and inefficient cooking systems. Solar lamps allow children to work on their homework after dark, solar cookers allow families to cook without polluting their homes with dangerous emissions. Investment in these kinds of technologies and distribution to those most in need can be life changing.
Modern renewables power 30% of all electricity, but that figure remains low for heating and transport. Work still needs to be done to improve solar power efficiency, storage, and widespread application in these sectors. Solar thermal energy, solar roads, cars, and ships have already been invented. At the rate the industry has been developing we expect these percentages to be much higher in the coming years.
Author: Rachael Mellor 13.08.24 licensed under CC BY-ND 4.0
For more information on Solar Power see below ⬇️
Info on SOLAR Energy
- News[29]
- General Info[39]
- Organizations[25]
- Solar Power Plants & Projects[65]
- Companies & Industry Network Federations[28]
- Feed-in Tariffs[21]
- Photovoltaics: Sun into Electricity[24]
- Sun into Heat[22]
- Solar energy storage and on-site consumption[35]
- Solar Cookers[54]
- Solar Lamps[21]
- Solar Cars
- Solar Planes[20]
- Solar Roads[30]
- Solar Ships[40]
- Solar Energy Costs[41]
- Sun into Homes - Light[6]
- Selected Articles[176]